Welcome to India Centre for Lab Grown Diamond (InCent-LGD), where we aim at bridging the industry needs and future of lab grown diamonds with our core technical expertise and advanced research facilities.

Raman spectroscopy serves as an effective, non-invasive method for examining material structure and assessing its quality. It is applied technique for characterizing diamond and graphite materials.
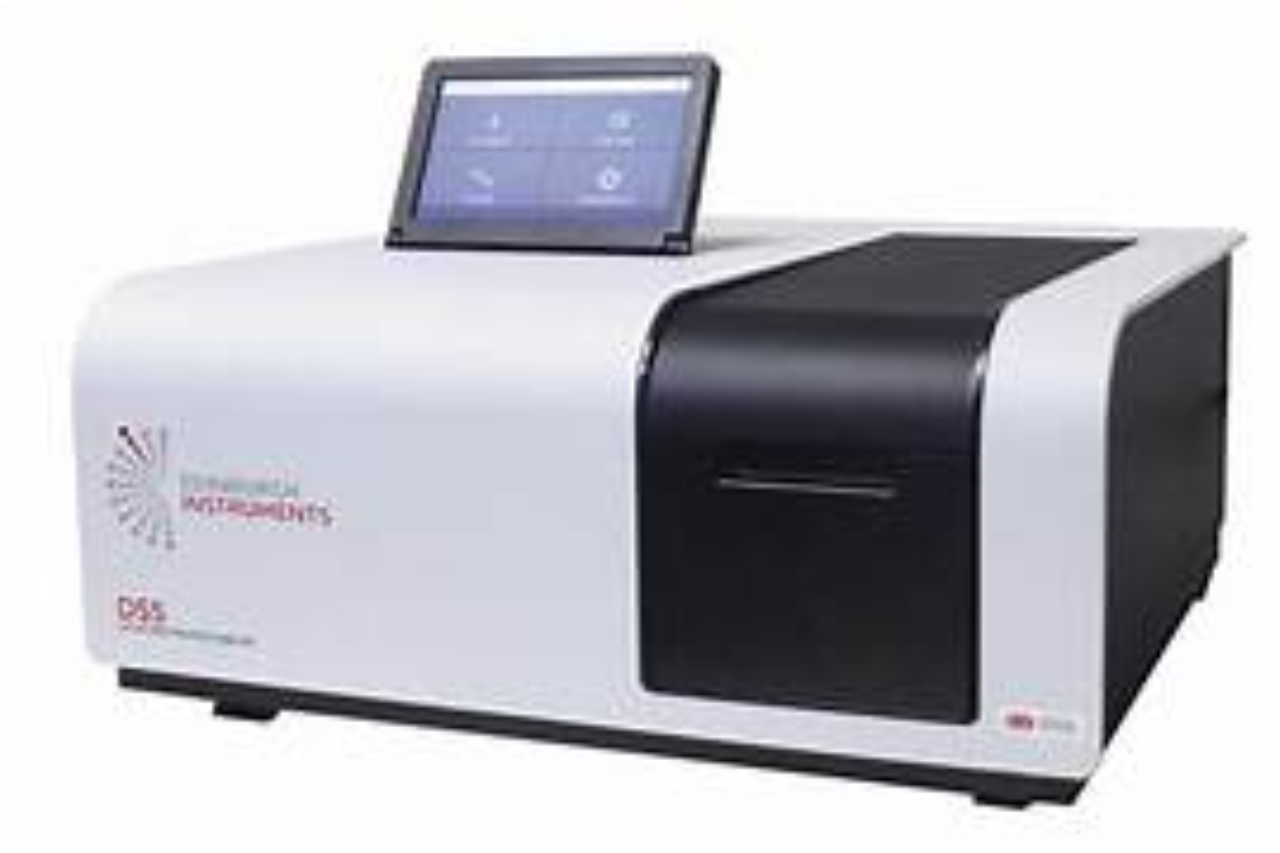

UV-Vis-NIR Spectroscopy is used to measure how much a chemical substance absorbs (transmitted) light. Nitrogen content of diamond can be determined by UV-Vis-NIR Spectroscopy.
The importance of nanoindenter mainly from the fact that mechanical properties of the diamond can be obtained directly from the indentation load and load-displacement measurements.

The electron is used as a source to interact with the sample in a scanning electron microscope (SEM).

Photoluminescence occurs when the absorbed photons excite electrons within the material.
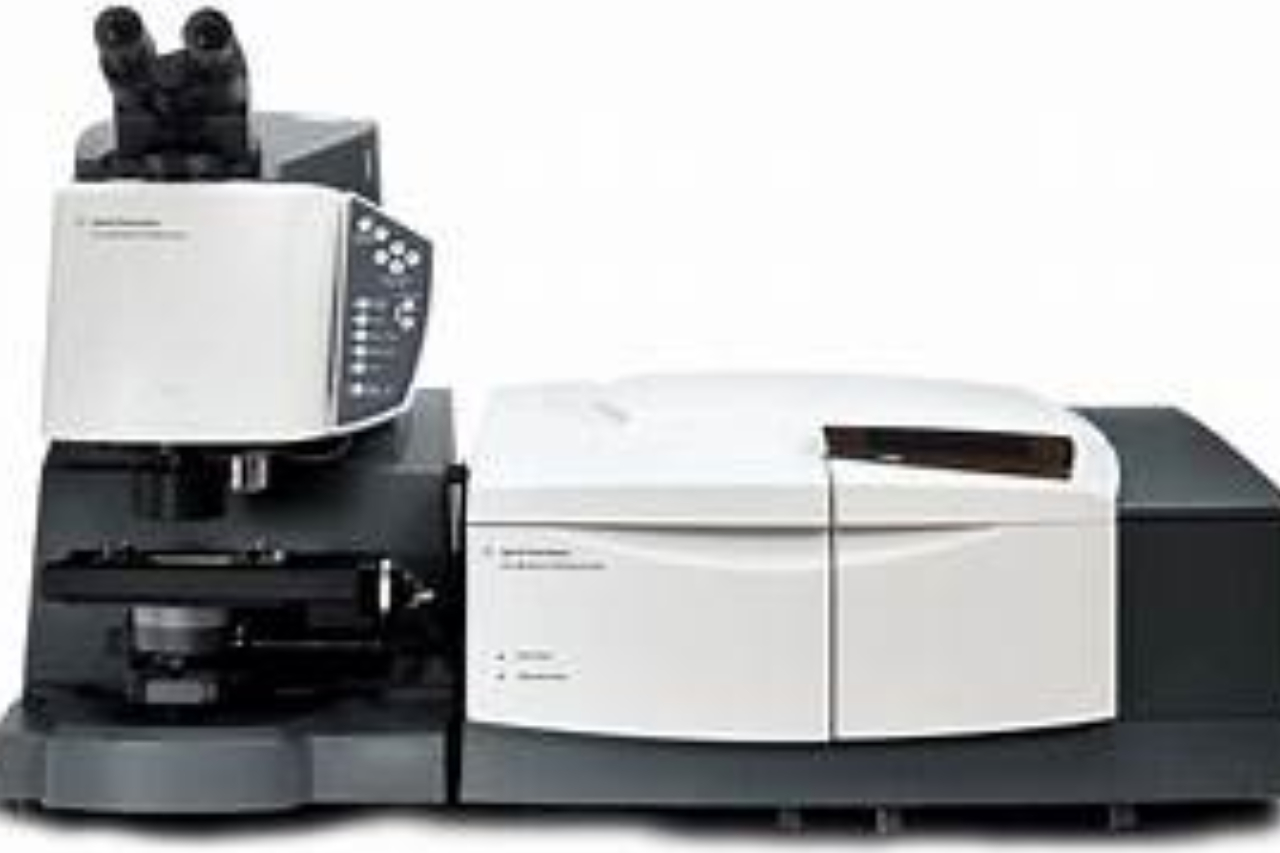

The molecule-related spectral information is obtained through Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy.
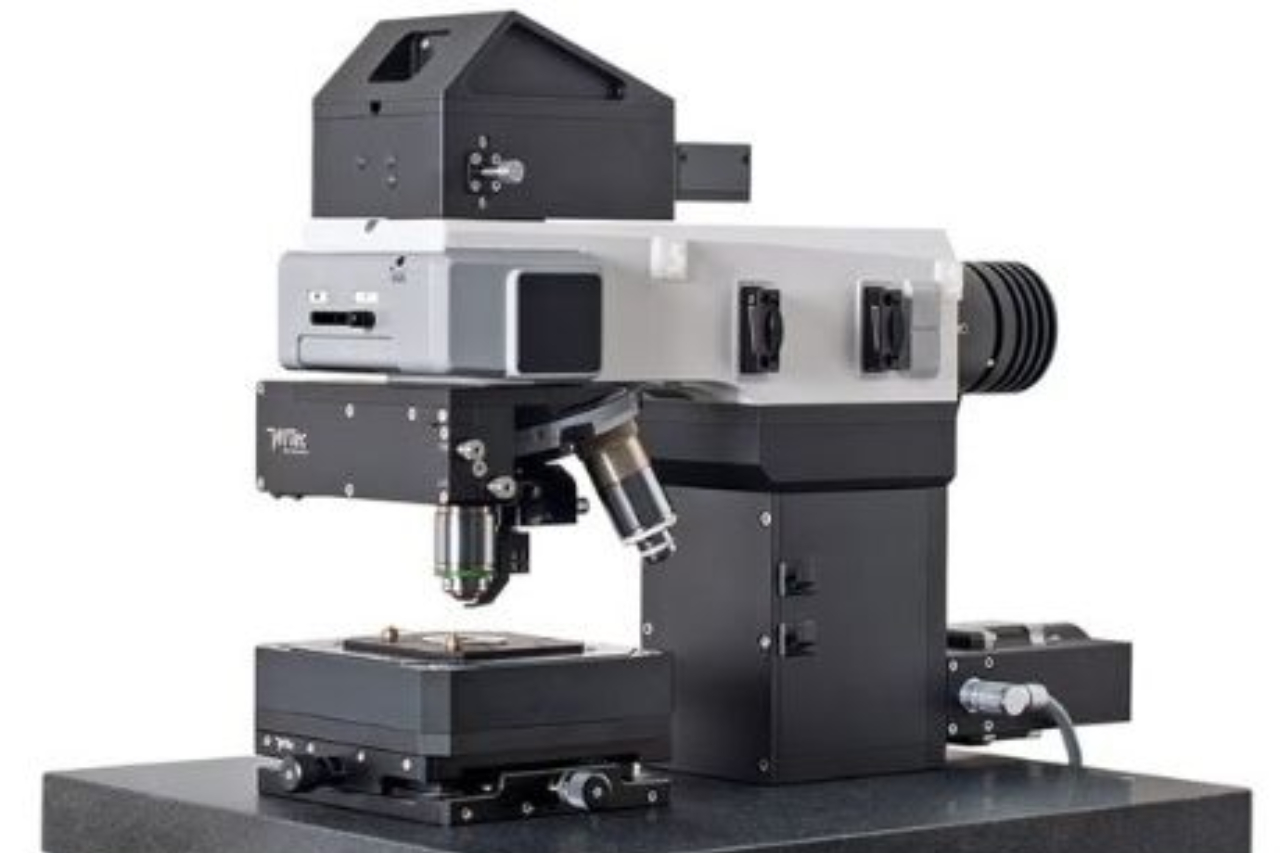

Surface features and topological variations of the single crystal diamond can be studied using atomic force microscope.

Surface features and topological variations of the single crystal diamond can be studied using atomic force microscope.

Surface features and topological variations of the single crystal diamond can be studied using atomic force microscope.

Surface features and topological variations of the single crystal diamond can be studied using atomic force microscope.
India Centre for Lab Grown Diamond (InCent – LGD)